Understanding Vehicle Suspension Systems
When you go about your day driving, you don’t think too much about your vehicle’s suspension systems. Not until you feel a bump that makes you uneasy or when your car starts to drift on the side. Your car’s suspension system does more than absorb bumps and jolts. The system is responsible for stability, control, and safety for you and everyone on the road. According to New Zealand Transport Agency Waka Kotahi, the suspension needs regular maintenance such as the tyres stay in contact with the road and the vehicles remain within safe boundaries.
Today, we’re going to take a look at the importance of vehicle suspension systems, the main components, and how they operate together, and when to get professional assistance.
What is a Vehicle Suspension System?
The vehicle suspension system is essentially the connection between your vehicle’s body and its wheels. It helps you steer your vehicle safely, supports your car's weight, absorbs shocks, and maintains the stability of your tyres on the road. According to the NZTA inspection webpage, steering and suspension must be properly maintained within safe tolerance.
What does the suspension system in a vehicle do? Think of your vehicle suspension system as a safety rail that keeps you comfortable during rides. Whenever you hit a bump on the road or drive over a pothole, your suspension keeps your car manageable and ensures a smooth ride.
Components of a Suspension System
Vehicle suspension technology and design consist of several parts, and let’s take a look at what they do.
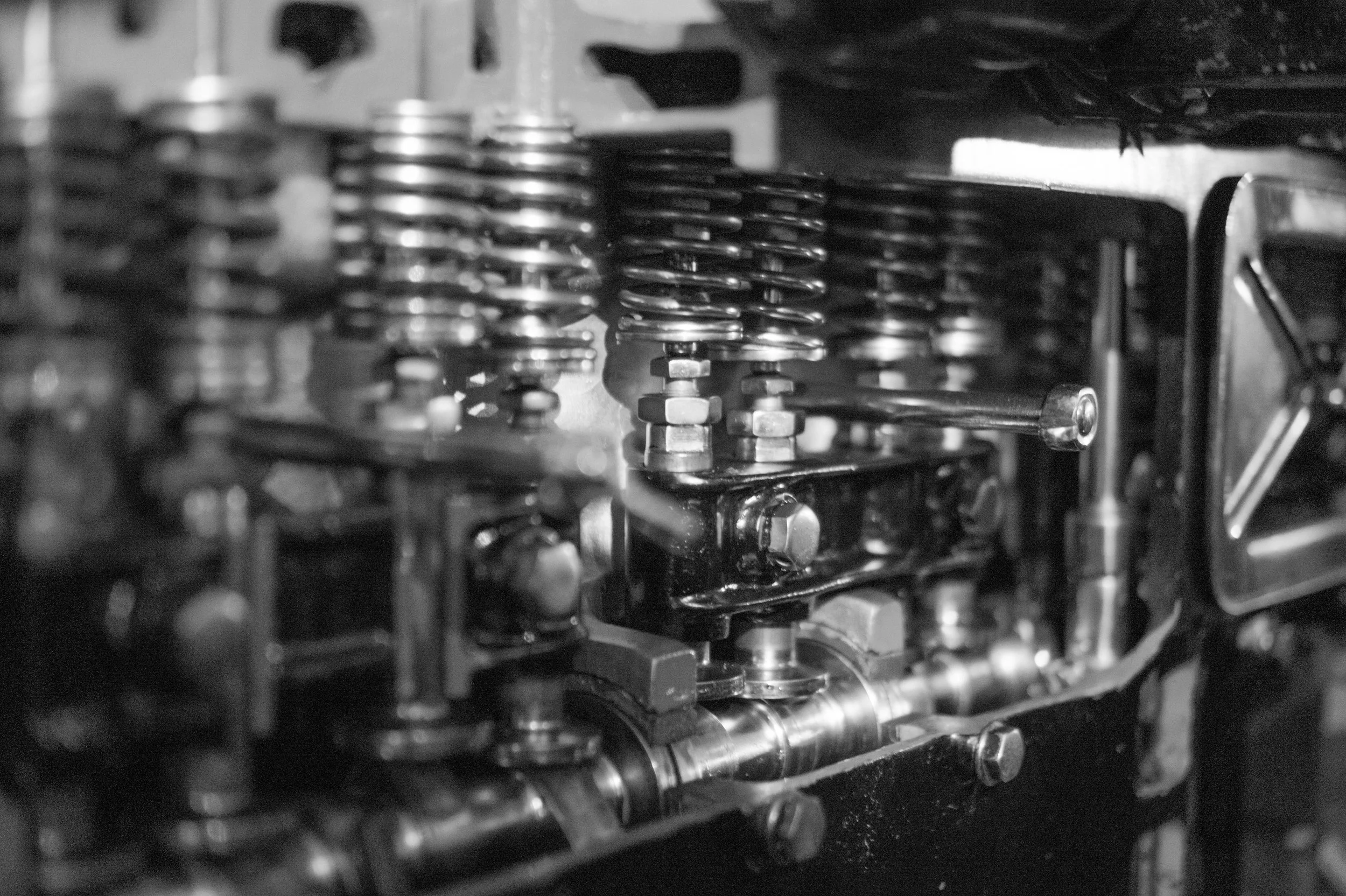
Springs
The springs have a vital role in a car suspension system. Their main function is to absorb shocks from road friction and keep everyone in the car comfortable. If your car doesn’t have any springs, your car will drive wobbly.
There are different types of springs, which includes: coil springs, leaf springs, and torsion bar springs.
Shock Absorbers (Dampers)
Shock absorbers or dampeners limit the absorbed shocks from the springs, reducing the movements caused by shocks and vibrations from the road. Without dampers, you’ll notice your car bouncing after a bump on uneven roads. Repairing shock absorbers is not recommended, a full, usually costly replacement, is a better long-term solution.
Struts
In many modern cars, the struts are part of the suspension system, along with the shock absorber and other components. They contain absorbers or damper functions to support the vehicle’s weight and shape. If your car’s struts wear out, you’ll experience awful handling and uneven tyre damage. Struts also serve as structural support for the vehicle’s suspension system.
Controls Arms & Bushings
The control arms or wishbones connect the wheels and suspension to your vehicle’s chassis, allowing movement up and down while keeping the wheels aligned. Bushings ease contact between metals, reducing noise and vibration; worn bushings or wishbones can cause knocking noises and handling concerns.
Ball Joints
The steering knuckles are connected to the suspension system by the ball joints. When you’re turning your vehicle, the ball joints pivot like the bones in the human hip do. These components provide stability and flexibility whenever you turn or need to swerve away from an obstacle. If your car’s ball joints are worn-out or damaged, you’ll notice whenever you drive over bumps you’ll hear clunking and knocking noises.
When ball joints completely break, you’ll risk losing control of your vehicle, and eventually lead to accidents.
Sway (Anti-Roll or Stabiliser) Bars
Sway bars, sometimes referred to as anti-roll or stabiliser bars, help in balancing your car whenever it turns or corners. By joining the left and right suspension systems, the sway bars manage the stability and balance of your car. Your car would tilt excessively in turns without them, making handling risky.
Poor cornering, uneven steering, and knocking noises are often caused by worn or broken sway bars. Getting frequent checks by a reliable mechanic helps avoid faulty sway bars and guarantees safer driving.
Common Signs of Suspension Problems
You should never overlook problems with your vehicle’s suspension system. Keep an eye out for the following warning signs, particularly on Dunedin’s local roads:
When you hit the brakes, your car’s front end drops, or ‘nose-dives.’
The ride bounced a lot even after stopping.
Tyres wear out quickly or get uneven.
Steering doesn’t seem tight while pulling or drifting in turns.
The shocks or struts that have visible oil leaks when they should be dry.
Noises that knock or clunk on rough surfaces or curves.
Any of these signs show that your suspension system is not working at its best, which compromises the handling and safety of your vehicle.
Why Suspension Systems are Essential for Safety and Performance
WoF suggests getting your car checked once a year or every 20,000 to 30,000 kilometres. The twisting and uneven roads of New Zealand mean you need to have a car that’s in tip-top shape.
Vehicle suspension wears out over time, and usually, they are overlooked until a serious problem comes up. Annual checks by a reliable workshop are important especially in winding, narrow, and hilly roads like in Dunedin. You must take every precaution to drive safely.
Getting Professional Help for Your Suspension Needs
The springs, shock absorbers, struts, control arms and bushings, ball joints, and the sway work together as a vehicle suspension system. When problems occur, you can take early action by being mindful of each part.
At Sims Brakes, we recognise the specific demands of Dunedin’s roads on automobiles, from steep hills to damp coastal roads. Our team pays close attention to how all of the suspension components work with your car’s brakes and steering system.
Don’t compromise your safety! Here at Sims Brakes, we’ll have your car in working order and running smoothly on Dunedin’s roughest roads. Get in touch with us today.